
But these areas can also tell us a bit about function. Generally, when neuroscientists talk about the lobes, they are doing so to denote a general anatomical location of brain activity. The cerebral hemispheres are further subdivided into four major lobes: the occipital, towards the back of the brain the parietal, just above the ear the temporal, just behind the forehead temples and the frontal, resting above the eyes at the very front of the cortex. Otherwise, the two cerebral hemispheres are nearly symmetrical. (Those areas may be on the right side in some left-handed individuals). Two key areas involved in language-Broca’s Area, responsible for language grammar and syntax, and Wernicke’s Area, implicated in language content and meaning processing-reside on the left side of the brain for most. While several popular books suggest these two sides of the brain are important to specific functions-that is, the right side of the brain is responsible for creativity while the left side handles your more analytical-type processing (sometimes referred to as “lateralization”)-activity for most cognitive tasks is seen on both hemispheres. These two sides of the brain are connected by the corpus callosum, a bridge of wide, flat neural fibers that help relay signals between them. The cerebral cortex is divided into two hemispheres.
/bainstem-572261475f9b58857dc36e2e.jpg)
The parts of the CNS work together seamlessly in healthy individuals, allowing the brain to govern functions and behaviors ranging from breathing to reading. This is probably what you think of when you picture the brain-and it is responsible for sensory perception, information processing, and memory, learning, and decision-making. Finally, perched above the brain stem and cerebellum, is the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum, the so-called “little brain,” next to the brain stem, handles balance and coordination of movement. It also helps conduct information from the brain to the PNS. The brain stem is responsible for autonomic processes, or processes that occur reflexively, like breathing and heart rate. But the CNS may also be discussed in terms of these three sections: the brain stem, the cerebellum, and the cerebral hemispheres. Some further break down the CNS into the hindbrain, the lower part of the brainstem the midbrain, the central part of the brainstem and the forebrain, which includes the cerebral hemispheres. The nervous system has two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), made up of the spinal cord and the brain and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the nerves and other types of supporting cells that branch throughout the rest of the body and communicate back to the CNS. The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that carry messages to and from the brain to the rest of the body.
FUNCTION OF THEBRAIN STEM FULL
While a complete discussion of neuroanatomy is worthy of a thick textbook full of elaborate illustrations, here are some of the basics.
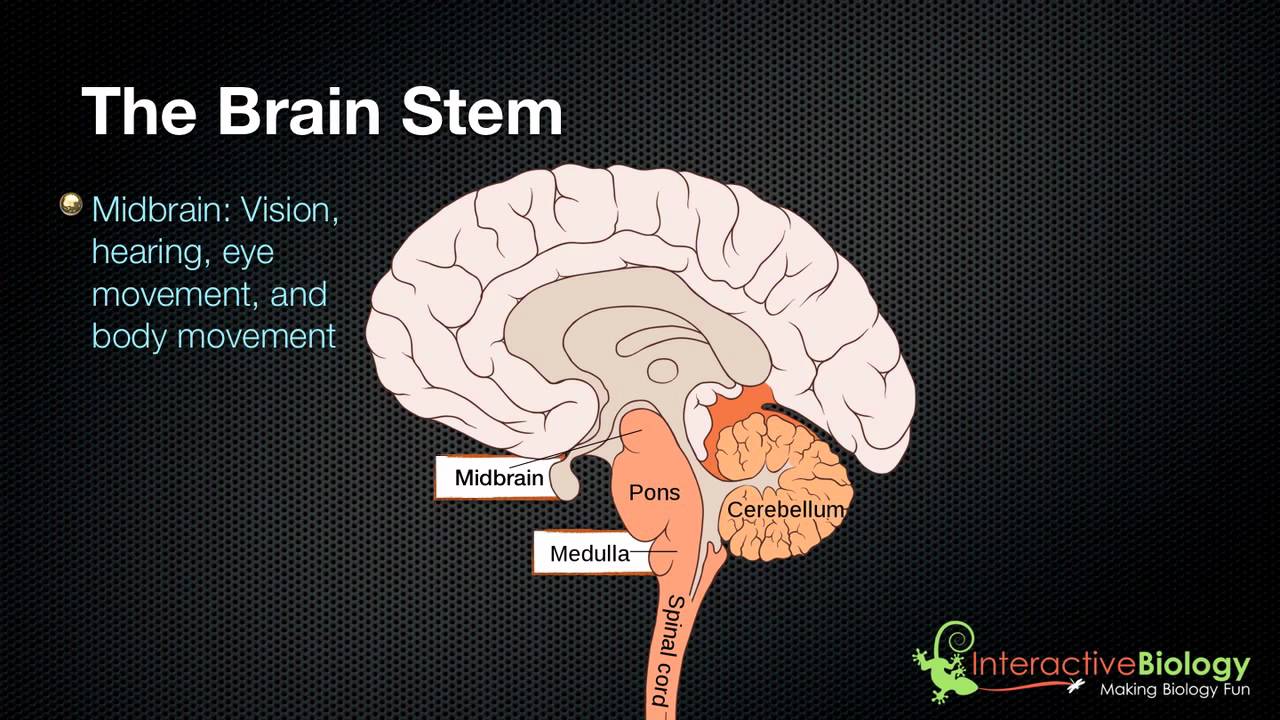

Each part of the brain’s intricate configuration works together to govern sensation and perception, information processing, and the initiation of a wide variety of behaviors-and helps us make sense of the world around us. Over the past few hundred years, scientists have learned that the brain has dedicated regions responsible for specific tasks like understanding and producing speech or processing visual and spatial information.
Its unique (and complex) three-dimensional architecture plays an important role in deciding upon and issuing those important commands. This specialized organ is responsible for every thought, every feeling, and the vast majority of our actions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
